Defining Attributes
Attributes are the foundation of Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC). They are key-value pairs that define characteristics of users, resources, and tenants, enabling you to create flexible and dynamic access control policies. By defining and managing attributes, you can create sophisticated authorization rules based on any combination of these characteristics.
Types of Attributes
Permit supports attributes on three different objects:
- User Attributes - Characteristics of the actor performing an action, to be used in dynamic roles (AKA user sets).
- Resource Attributes - Characteristics of the resource the action is being performed on, to be used in dynamic resources (AKA resource sets).
- Tenant Attributes - Characteristics of the tenant containing the actor and the resource. Can be used in user sets of users that appear in the tenant.
- Role Attributes - Metadata that lives on RBAC roles. Use them to tag roles with dimensions such as tier, geography, or product area and to filter or search roles via the API (for example with the
attr_filters in the List Roles API).
Defining Attributes
Attributes can be assigned in three ways:
- Assign attributes to users and tenants directly from the UI or the API
- Push user and resource attributes in the permit.check call
- Write a short custom Rego function that generates all types of attributes on the fly
Note that not all attribute sources are available for all attribute types, for example resource attributes can only be pushed in permit.check and as a custom Rego function.
Define Stored User Attributes
After creating the attribute definitions, you can define user-specific attributes via the UI or API.
In the UI: Go to Directory → Tenant settings (top-right settings button) → User Attributes to create or edit user-attribute definitions. Then, within the Directory, open an individual user and use Edit Attributes to set that user’s values.
Via API / SDK: update the user object with an attributes payload when calling the relevant endpoint (permit.api.users.update(...), permit.api.users.sync(...), etc.).
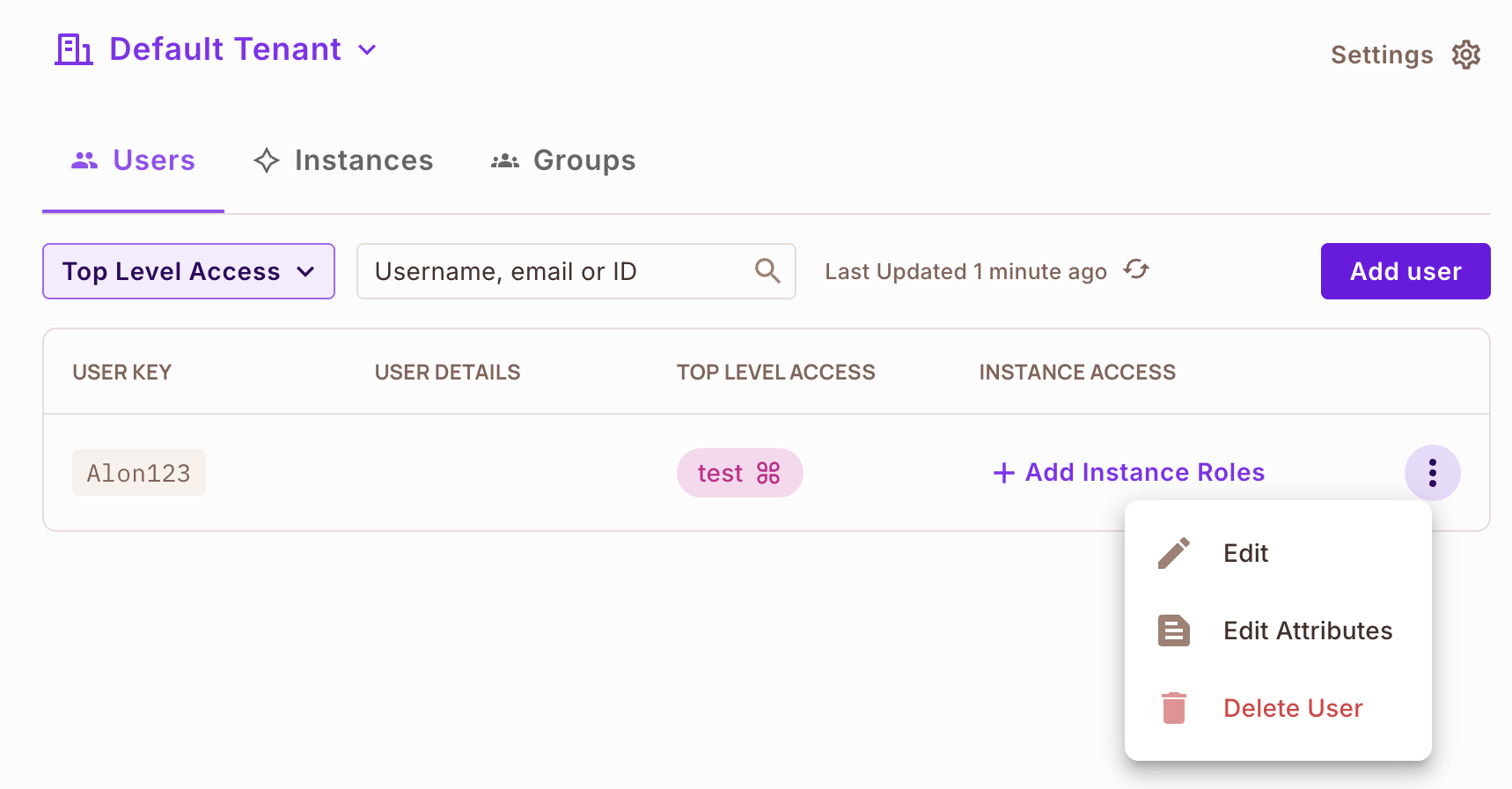
From this window you can edit the user attributes as JSON.
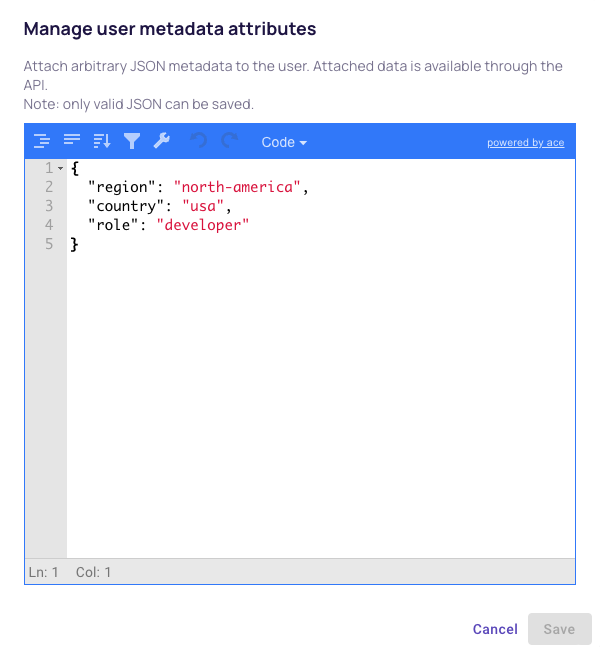
Note that to add new attributes you need to first create attribute definitions.
Define Stored Tenant Attributes
After creating the attribute definitions, you can define tenant-specific attributes either in the UI or through the API.
In the UI: Navigate to Directory → Tenant settings (top-right settings button) → Manage tenants, choose the tenant, and open the Tenant Attributes panel to edit metadata.
Via API / SDK:
curl -X PATCH 'https://api.permit.io/v2/facts/{project_id}/{env_id}/tenants/{tenant_key}' \
-H 'Authorization: Bearer API_SECRET_KEY' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{
"attributes": {
"tier": "enterprise",
"plan_version": "2026-01"
}
}'
Send any metadata needed for policy decisions in the attributes object.
Define Role Attributes
Role attributes can be defined in the UI or managed via the Roles API.
In the UI: Go to Directory → Tenant settings (top-right settings button) → Role Attributes to tag roles with metadata.
Via API / SDK: include an attributes object when creating or updating a role. For example:
curl -X PATCH 'https://api.permit.io/v2/schema/{project_id}/{env_id}/roles/{role_key}' \
-H 'Authorization: Bearer API_SECRET_KEY' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{
"attributes": {
"tier": "gold",
"department": "finance"
}
}'
Once attributes are stored, you can filter roles (for example, ?attr_tier=gold) or retrieve the metadata through the role APIs. This is especially useful when delegating tenant-specific role management or when you need to build automation around role categories.